Last Updated on March 13, 2024 2:58 pm by Laszlo Szabo / NowadAIs | Published on March 13, 2024 by Laszlo Szabo / NowadAIs
Meet Google’s Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) – AI agent for 3D virtual environments – Key Notes
- SIMA capable of navigating and learning within multiple virtual environments simultaneously.
- Designed to understand and execute complex instructions in diverse settings, enhancing its adaptability and utility.
- Aims to bridge the gap between AI’s theoretical capabilities and practical applications across various industries.
- SIMA’s development marks a significant step toward achieving general AI systems, capable of performing tasks across different domains with little to no human intervention.
- Its technology promises to enhance video game design, simulation-based learning, and virtual experimentation, offering a more immersive and interactive experience.
Google’s Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) on Board
In the ever-evolving landscape of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Google DeepMind has made significant strides in developing advanced AI systems. One such breakthrough is the Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA), by Google Deepmind, a versatile AI agent that can navigate and comprehend a variety of 3D virtual environments.
Now we delves into the fascinating world of SIMA, exploring its capabilities, training methodologies, and potential applications.
The Significance of Video Games in AI Research
Video games have become a crucial testing ground for AI systems, offering rich learning environments with real-time settings and dynamic objectives. Google DeepMind’s journey in AI and gaming has been remarkable, starting from their early work with Atari games to the development of AlphaStar, an AI system that can play StarCraft II at a human-grandmaster level. With SIMA, DeepMind aims to shift their focus from individual games to building a general, instructable game-playing AI agent.
Training SIMA in Diverse Gaming Worlds
To equip SIMA with the ability to understand and follow natural-language instructions in various gaming environments, Google DeepMind collaborated with eight game studios and trained SIMA on nine different video games. These games included popular titles such as “No Man’s Sky” by Hello Games and “Teardown” by Tuxedo Labs. Each game in SIMA’s portfolio presented a unique interactive world, requiring the agent to learn skills ranging from basic navigation to complex tasks like spaceship piloting or resource mining.
Alongside partnerships with game developers, DeepMind also developed four research environments, including the Construction Lab built with Unity. These research environments further enhanced SIMA’s understanding of object manipulation and intuitive comprehension of the physical world. To train SIMA, pairs of human players were observed, with one player instructing the other while playing the game. This approach allowed DeepMind to record instructions that would lead to specific game actions, enabling SIMA to learn the association between language and gameplay behavior.
The Architecture and Functionality of SIMA
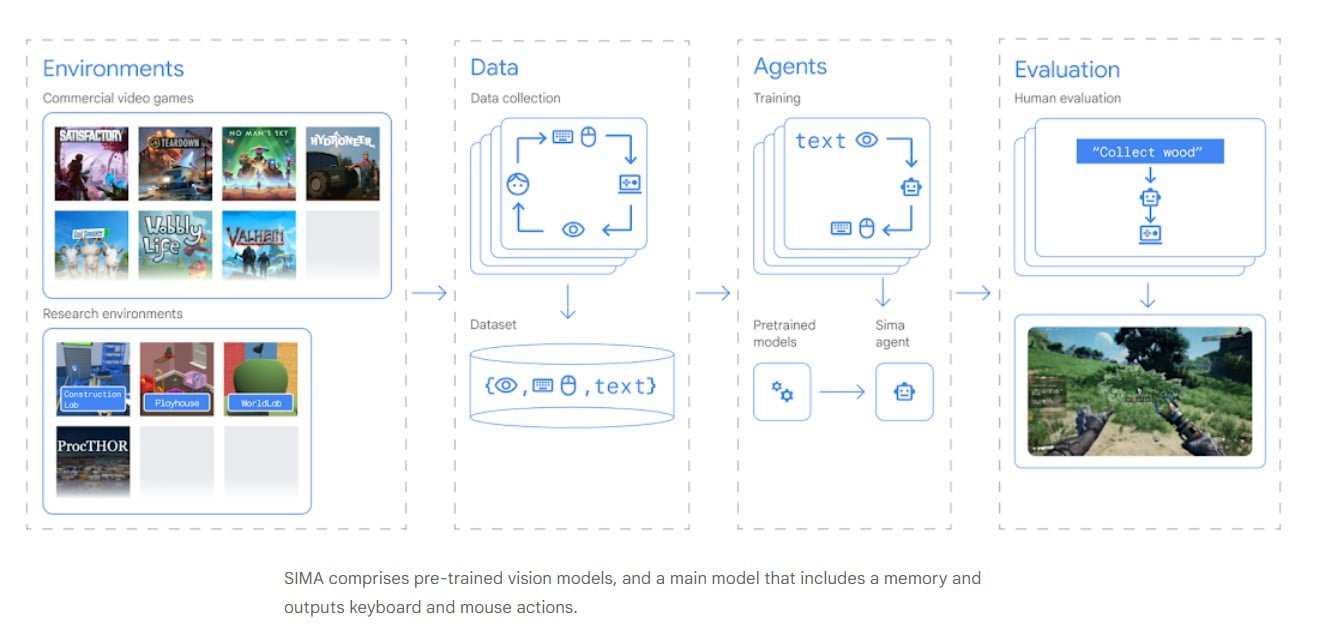
SIMA comprises pre-trained vision models, a memory component, and outputs for keyboard and mouse actions. The AI agent can perceive and comprehend a wide range of environments, allowing it to execute instructed goals. SIMA’s model is specifically designed for precise image-language mapping, while its video model predicts on-screen events. DeepMind finetuned these models using training data relevant to the 3D settings in SIMA’s portfolio.
One notable aspect of SIMA is its simplicity of interaction. Unlike other AI agents, SIMA does not require access to a game’s source code or bespoke APIs. It only needs two inputs: on-screen images and simple, natural-language instructions provided by the user. By utilizing keyboard and mouse outputs, SIMA can effectively control the central character in a game to carry out the given instructions. This user-friendly interface enables SIMA to potentially interact with any virtual environment, making it a versatile AI agent.
Evaluating SIMA’s Skills and Generalization Abilities
DeepMind evaluated SIMA’s performance across 600 basic skills, including navigation, object interaction, and menu use. These skills were designed as simple tasks that could be accomplished within approximately 10 seconds. While SIMA demonstrated proficiency in these tasks, the ultimate goal for DeepMind is to develop agents capable of tackling complex tasks that require high-level strategic planning and multiple sub-tasks.
In their evaluations, DeepMind discovered that SIMA agents trained on a set of nine 3D games significantly outperformed agents trained solely on each individual game. Additionally, SIMA agents trained on all but one game performed nearly as well on the unseen game as agents trained specifically for it. This ability to function effectively in new environments demonstrates SIMA’s potential for generalization beyond its training, a noteworthy achievement in AI research.
The Importance of Language in SIMA’s Performance
Language plays a crucial role in SIMA’s performance. In a control test where the agent was not given any language training or instructions, it behaved in an appropriate but aimless manner. For instance, the agent tended to gather resources rather than following specific instructions on where to go. DeepMind’s evaluation of SIMA’s ability to follow instructions involved nearly 1500 unique in-game tasks, with human judges providing valuable feedback. When compared to environment-specialized agents, SIMA showcased its proficiency as a generalist agent trained across multiple environments.
Advancing AI Agent Research with Google’s Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA)
The results obtained from SIMA’s development and evaluation highlight the potential for building a new generation of generalist AI agents driven by language. While this research is still in its early stages, DeepMind aims to expand SIMA’s training environments and incorporate more capable models. As SIMA is exposed to a wider range of training worlds, its generalizability and versatility are expected to improve. With more advanced models, DeepMind envisions enhancing SIMA’s understanding and ability to act on higher-level language instructions, enabling the agent to accomplish more complex goals.
Conclusion: Towards General AI Systems
Google DeepMind’s Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) has emerged as an exciting development in the field of AI. SIMA’s ability to comprehend and navigate various 3D virtual environments based on natural-language instructions showcases its potential to become a valuable tool in numerous domains. While there is still much research to be done, SIMA represents a step forward in building more general AI systems that can undertake a wide range of tasks in a way that is helpful to people online and in the real world.
Definitions
- Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA): An advanced AI system designed to operate, learn, and adapt across multiple virtual environments. It represents a significant advancement towards creating versatile AI that can handle a wide range of tasks and scenarios with minimal human input.
- Google DeepMind: A leading AI research organization that focuses on creating AI that can learn and master any task. It is renowned for its breakthroughs in AI, including the development of AI that can outperform humans in complex games.
- General AI Systems: AI that possesses the ability to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide range of tasks, not limited to a single domain or set of tasks. It contrasts with narrow AI, designed to handle specific tasks.
- Video Games: Digital games involving human interaction with a user interface to generate visual feedback on a video device. They range from simple text-based environments to complex virtual worlds.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What makes the Scalable Instructable Multiworld Agent (SIMA) unique in the AI landscape?
- SIMA stands out for its ability to operate and learn in multiple virtual environments, offering unparalleled versatility and adaptability in AI technology.
- How can SIMA impact the future of video games?
- By incorporating SIMA, game developers can create more dynamic, responsive, and complex game environments, significantly enhancing player engagement and experience.
- What role does SIMA play in advancing General AI Systems?
- SIMA represents a step toward achieving general AI by demonstrating the capability of an AI system to learn and adapt across various domains without extensive reprogramming.
- How does SIMA learn to navigate different worlds?
- SIMA utilizes advanced machine learning algorithms and natural language processing to interpret instructions and learn from interactions within each environment, continuously improving its performance.
- Can SIMA interact with humans within these multiworld environments?
- Yes, SIMA is designed to understand and execute complex instructions from humans, allowing for interactive and collaborative experiences within virtual worlds.