Last Updated on July 8, 2024 11:17 am by Laszlo Szabo / NowadAIs | Published on July 8, 2024 by Laszlo Szabo / NowadAIs
AI Transforms Thoughts into Images Through Mind-Reading – Key Notes
- AI technology converts thoughts into images with near-perfect accuracy.
- Developed by researchers from Radboud University, Netherlands.
- Uses brain signal recordings and an upgraded AI system for image reconstruction.
- Experiments conducted with fMRI machines and macaque monkeys.
- Potential applications in vision impairment treatments and communication for disabilities.
- The system uses predictive attention mechanisms for neural decoding.
- Significant implications for neuroscience and AI integration.
Thoughts into Images: Mind Reading in Progress
A new AI technology is capable of converting thoughts into images with exceptional precision, achieving almost perfect accuracy in replicating the original images based on brain signals. According to Thirza Dado’s tweet, a major advancement has been made in the realm of neuroscience and artificial intelligence (AI) as scientists have successfully recreated images based on brain activity.
Our preprint on “PAM for #neuraldecoding of #visualperception” is featured on @newscientist! 🧠📖♥️
w/ @umuguc (https://t.co/t7KZeO6546) @DondersInst https://t.co/gBYTmsb2ih(Preprint: https://t.co/EnqT2H69Ib)#attentionmechanism #brainreading pic.twitter.com/dsjchoBjGE
— Thirza Dado (@ThirzaDado) July 4, 2024
Using an upgraded AI system for mind-reading, they were able to generate reconstructed images that were the “closest” matches, especially when utilizing direct recordings of brain signals.
The impressive achievement was carried out by researchers from Radboud University in the Netherlands. They combined their previous study with the most recent research to produce precise reconstructions.
“According to my understanding, these are the most precise and nearest reconstructions”
stated by Umut Guçlu, a part of the team that conducted the research. The advancement of this mind-reading technology has the ability to open up possibilities for novel treatments for individuals experiencing vision impairment.
Images Read Out
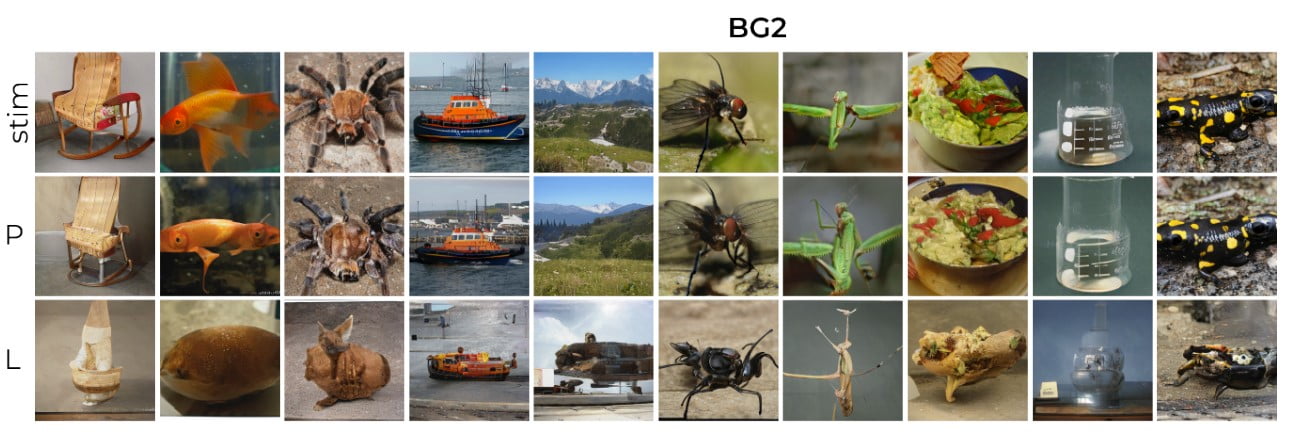

Two separate experiments were carried out by the team. For the initial study, a small group of participants were positioned inside an fMRI machine to measure variations in blood flow in the brain. This method is commonly used to analyze brain function.
During the experiment, the participants were presented with facial images and their brain activity was recorded by the fMRI in the visual area. This data was then inputted into the artificial intelligence (AI) program. The results showed that the AI successfully recreated the images, closely resembling the original ones.
In a subsequent experiment, data from previous trials were reexamined wherein an array of electrodes was inserted into a macaque monkey’s brain to monitor its responses while viewing artificially generated images.
The updated AI successfully reconstructed the initial images with almost flawless precision. The images generated from the monkey’s brain activity closely resembled the original images.
After conducting the experiments, the scientists utilized an advanced AI system to examine the brain activity data. This particular AI system possessed the ability to learn and determine the specific areas of the brain to concentrate on.
Various uses and applications
The technology has a wide range of applications across different domains. In the AI healthcare industry, it has the potential to improve vision by stimulating the brain to generate more vivid visual experiences for people with visual disabilities.
In addition, it holds the capability to transform communication for people with disabilities by offering new opportunities for interaction and self-expression.
The researchers concluded in their study that with the rapid advancements in generative modeling, this framework has the potential to produce even more remarkable reconstructions of perception and potentially even imagery in the near future.
Definitions
- PAM (Predictive Attention Mechanism): A method used in AI to focus on relevant parts of brain signals to decode visual perceptions.
- Brain Signals: Electrical impulses generated by neurons in the brain, used to convey information about thoughts and sensory inputs.
- Neuroscience: The scientific study of the nervous system, including the brain, to understand its structure, function, and disorders.
- Radboud University: A prominent research university located in Nijmegen, Netherlands, known for its contributions to science and technology.
- fMRI Machines: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging machines that measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the “Thoughts into Images” technology? “Thoughts into Images” refers to AI technology that converts brain signals into visual images. It uses predictive attention mechanisms to accurately decode and reconstruct images from brain activity data.
2. How does the “Thoughts into Images” technology work? The technology records brain signals using fMRI machines or electrode arrays. These signals are then processed by an advanced AI system, which reconstructs the visual images that closely match the original stimuli viewed by the subject.
3. Who developed the “Thoughts into Images” technology? This technology was developed by researchers at Radboud University in the Netherlands. Their work combines neuroscience and artificial intelligence to achieve high-precision image reconstruction.
4. What are the potential applications of “Thoughts into Images” technology? Potential applications include improving vision for individuals with visual impairments and offering new communication methods for people with disabilities. It may also enhance our understanding of visual perception and brain function.
5. What experiments were conducted to test the “Thoughts into Images” technology? Researchers conducted experiments using fMRI machines on human participants and electrode arrays on macaque monkeys. Both experiments successfully reconstructed images based on brain activity, demonstrating the technology’s precision and effectiveness.